Introduction to C
C is a general-purpose programming language developed in the early 1970s by Dennis Ritchie. C was designed to provide low-level access to memory while remaining portable across different systems. Because of this balance, C is widely used in operating systems, embedded systems, compilers, and performance-critical applications.An introduction to C language is often recommended as the first step for anyone serious about learning programming. Many popular languages such as C++, Java, and Python are influenced by C, making it an excellent starting point.
Features of C Programming Language
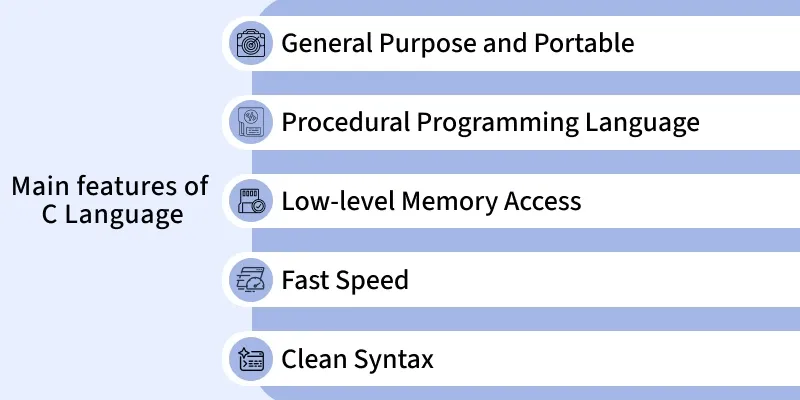
The C programming language is popular because of its powerful features and wide range of applications. Understanding the features of C helps beginners appreciate why it is still widely used in software development today.Below are the main features of C, explained based on the highlighted points.
1. General Purpose and Portable
C is a general-purpose programming language, which means it can be used to develop a wide variety of applications such as operating systems, databases, and embedded systems.It is also portable, meaning a program written in C can run on different machines with little or no modification.
2. Procedural Programming Language
C follows a procedural programming approach. Programs are divided into functions, and each function performs a specific task.This makes C programs easy to understand, test, debug, and maintain, especially for large applications.
3. Low-Level Memory Access
One of the most powerful features of C is its ability to access memory directly using pointers.This low-level memory control makes C suitable for system programming, device drivers, and embedded systems where performance and memory efficiency are critical.
4. Fast Speed
C is a compiled language, which means programs are converted directly into machine code.Because of this, C programs execute very fast and use system resources efficiently, making them ideal for performance-critical applications.
5. Clean Syntax
The syntax of C is simple, clean, and easy to learn.It uses a limited number of keywords and a structured format, which helps beginners write clear and readable programs.
Syntax of C Programming Language
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, World!");
return 0;
}Identifiers in C
In the C programming language, identifiers are the names used to identify variables, functions, arrays, and other user-defined elements in a program. Identifiers help the compiler and programmers distinguish one element from another.
Example:
int total;
float salary;
void calculateSum();
In the above examples, total, salary, and calculateSum are identifiers.
Rules for Naming Identifiers in C
To write valid identifiers in C, the following rules must be followed:
- An identifier must start with a letter (a–z or A–Z) or an underscore (
_). - It can contain letters, digits, and underscores.
- It must not start with a digit.
- No special characters such as
@,#,$, or spaces are allowed. - Keywords of C cannot be used as identifiers.
- Identifiers are case-sensitive (
countandCountare different).
Keywords in C
Keywords in C are special words recognized by the compiler. Each keyword has a fixed purpose and is part of the language syntax.
Example:
int number;Here, int is a keyword.
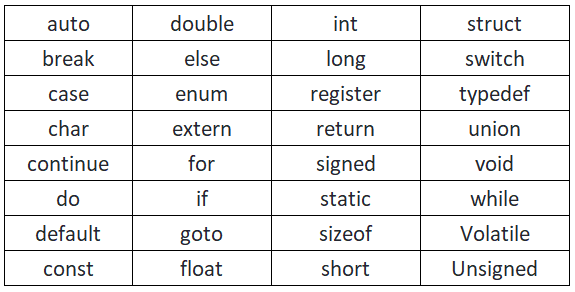
List of Keywords in C
C has 32 standard keywords:
Rules for Using Keywords in C
- Keywords cannot be used as identifiers
- Keywords are written in lowercase
- Each keyword has a predefined meaning
- Keywords are case-sensit
Variables in C
In the C programming language, a variable is a named memory location used to store data that can be changed during program execution. Variables allow programs to store, process, and manipulate data efficiently.
Example:
int age = 20;Here, age is a variable that stores an integer value.
Declaration of Variables in C
Before using a variable in C, it must be declared with a data type.
Syntax:
data_type variable_name;Example:
int number;
float price;
char grade;Initialization of Variables in C
Initialization means assigning a value to a variable.
int count = 10;
float salary = 25000.50;
char letter = 'A';Types of Variables in C
1. Local Variables
Declared inside a function and accessible only within that function.
void func() {
int x = 5;
}2. Global Variables
Declared outside all functions and accessible throughout the program.
int total;3. Static Variables
Retain their value between function calls.
static int count = 0;Data Types in C
Data types in C play a crucial role in program execution. They help:
- Allocate appropriate memory space
- Improve program performance
- Avoid logical and runtime errors
- Make code readable and maintainable
Understanding data types in C allows programmers to choose the right type for the right task.
Classification of Data Types in C
Data types in C are mainly divided into three categories:
- Basic Data Types in C
- Derived Data Types
- User Defined Data Types
Each category of data types in C serves a specific purpose in program development.
Basic Data Types in C
Basic data types in C are the fundamental building blocks used to store simple values. These data types in C are predefined and widely used.
Common basic data types in C include:
int– stores integer valuesfloat– stores decimal valuesdouble– stores double-precision floating-point valueschar– stores single characters
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int age = 20;
float marks = 85.5;
char grade = 'A';
printf("Age: %d\n", age);
printf("Marks: %.1f\n", marks);
printf("Grade: %c\n", grade);
return 0;
}OUTPUT
Age: 20
Marks: 85.5
Grade: A
These basic data types in C are essential for storing numeric and character data.
Derived Data Types in C
Derived data types are formed by using basic data types in C. These data types in C allow more complex data handling.
Examples of derived data types:
- Arrays
- Pointers
- Structures
- Unions
Derived data types in C help in storing multiple values and managing large amounts of data efficiently.
User Defined Data Types in C
User defined data types in C allow programmers to create their own data types according to program requirements. These data types in C improve code organization and reusability.
Common user defined data types include:
structunionenumtypedef
User defined data types in C are widely used in real-world applications to represent complex entities.
