Introduction to Java
Java is a popular high-level programming language developed in 1995 by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems. It is platform-independent, meaning Java programs can run on any operating system using the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Java is widely used for building web, mobile, and enterprise applications.
Features of Java
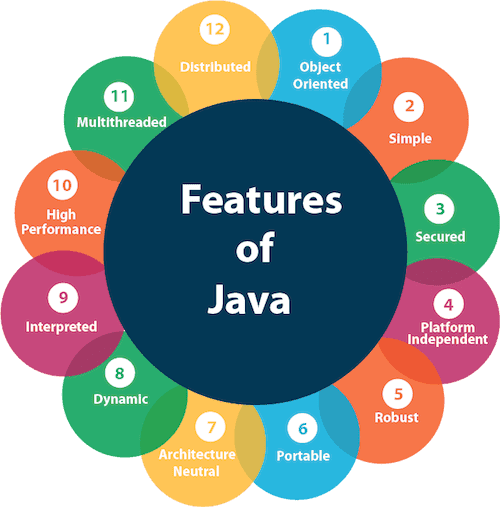
1. Object-Oriented
Java is an object-oriented language, which means it is based on objects and classes. It supports concepts like inheritance, polymorphism, encapsulation, and abstraction. This helps in writing reusable and well-structured programs.
2. Simple
Java is easy to learn and understand. It removes complex features like pointers and operator overloading, making it simpler than languages like C and C++.
3. Secured
Java is a secure language. It uses bytecode verification, class loaders, and a security manager to protect applications from viruses and unauthorized access.
4. Platform Independent
Java is platform independent, meaning a Java program can run on any operating system. This is possible because Java programs run on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
5. Robust
Java is robust because it has strong memory management, automatic garbage collection, and exception handling. These features help avoid system crashes and errors.
6. Portable
Java is portable because its bytecode can be executed on any machine that has a JVM. There is no need to modify the program for different systems.
7. Architecture Neutral
Java is architecture neutral, meaning it is not dependent on any specific hardware architecture. Java programs behave the same on all types of systems.
8. Dynamic
Java is dynamic in nature. Classes can be loaded at runtime, and memory is allocated dynamically, which makes Java flexible and adaptable.
9. Interpreted
Java code is first compiled into bytecode and then interpreted by the JVM. This allows Java programs to run on different platforms.
10. High Performance
Java provides high performance using the Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler, which converts bytecode into native machine code during execution.
11. Multithreaded
Java supports multithreading, which allows multiple tasks to run at the same time. This improves performance and is useful in applications like games and web servers.
12. Distributed
Java supports distributed applications using networking features like RMI and APIs. It helps in developing applications that work across multiple computers.
Identifiers in Java
An identifier in java is the name given to a programming element such as a variable, method, class, object, or package. In the java language, identifiers are used to identify these elements uniquely so that the compiler and programmer can easily refer to them.
For example
int marks;
class Student { }Here, marks and Student are identifiers in the java language.
Rules for Identifier in Java Language
The java language follows specific rules for creating a valid identifier in java:
- An identifier must start with a letter (A–Z or a–z), underscore (_), or dollar sign ($).
- It cannot start with a number.
- It can contain letters, digits, underscores, and dollar signs.
- Keywords of the java language cannot be used as identifiers.
- Spaces and special symbols are not allowed.
- Identifiers in the java language are case-sensitive.
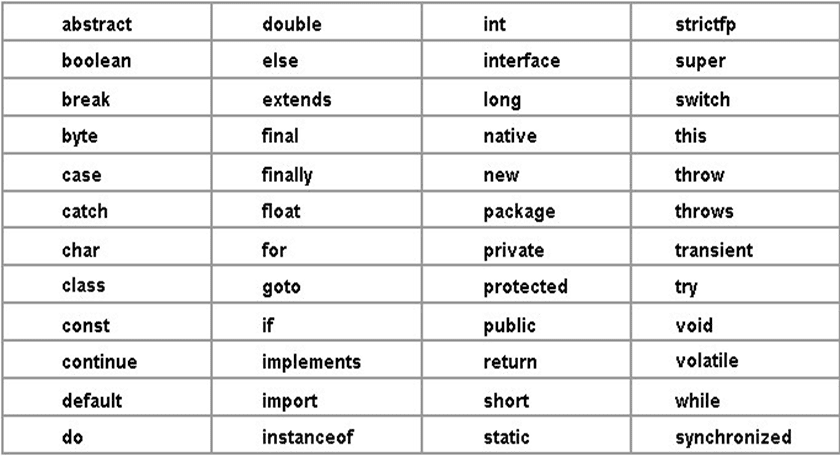
Keywords in Java
In Java, keywords are reserved words that have a special meaning predefined by the Java language. These keywords are used to perform specific operations and cannot be used as identifiers (names of variables, classes, or methods).
List of Common Keywords in Java
Variables in Java
A variable in Java is a name given to a memory location that is used to store data. The value of a variable can change during program execution. Variables help Java programs store, process, and manipulate data.
Syntax of Variable in Java
dataType variableName = value;Example:
int age = 20;Here, int is the data type, age is the variable name, and 20 is the value.
